5 Benefits of Intermittent Fasting and How It Works
Exploring the World of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting, a dietary approach gaining popularity, focuses not on what you eat, but rather when you eat. This intriguing method involves cycling between eating and fasting periods. By restricting your eating window, intermittent fasting can potentially aid in weight management, optimize hormone levels, and activate the body's natural healing processes.
Different Approaches to Intermittent Fasting

There are various methods to practice intermittent fasting, catering to different lifestyles, preferences, and goals. Here are some of the most prominent ones:
16/8 Method
In this method, you consume your meals within an 8-hour window and fast for the remaining 16 hours of the day.
5:2 Method
With the 5:2 approach, you maintain your regular eating habits for five days of the week but restrict your calorie intake to approximately 500-600 calories on the other two days.
Eat-Stop-Eat
This method involves a 24-hour fast once or twice a week, where you abstain from consuming any calories.
Warrior Diet
With the Warrior Diet, you primarily eat small portions of fruits and vegetables during the daytime and have a substantial meal in the evening.
Alternate Day Fasting
In this approach, you alternate between days of regular eating and days of fasting or very low-calorie intake.
The key to success with intermittent fasting is selecting the method that aligns best with your lifestyle, preferences, and long-term sustainability.
The Remarkable Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
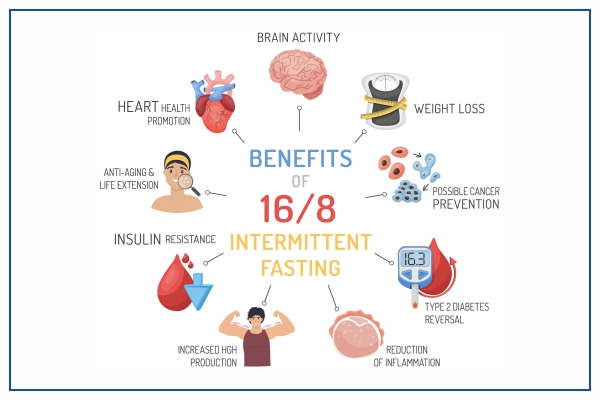
But why should you consider intermittent fasting? What are the tangible advantages of adopting this dietary pattern? Let's delve into five compelling reasons why intermittent fasting can positively impact your health and overall well-being.
Shedding Unwanted Pounds and Belly Fat
One of the most apparent benefits of intermittent fasting is weight loss. By reducing meal frequency and caloric intake, you create a calorie deficit that can lead to fat loss. Additionally, fasting can lower insulin levels and boost growth hormone levels, which promote fat-burning and muscle growth. Intermittent fasting also revs up your metabolism by increasing norepinephrine levels, stimulating the breakdown of fat cells.
Notably, intermittent fasting can specifically target stubborn belly fat, linked to various health concerns such as diabetes, heart disease, and inflammation. Studies reveal that this dietary approach can reduce waist circumference and visceral fat – the fat that surrounds vital organs.
Regulating Blood Sugar and Cholesterol Levels

Another significant advantage of intermittent fasting is its potential to enhance blood sugar and cholesterol profiles, critical factors in diabetes and cardiovascular disease management and prevention. Fasting can lead to lower blood glucose and insulin levels, improving insulin sensitivity and lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, intermittent fasting can reduce triglycerides and LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. It may even boost HDL (good) cholesterol levels, protecting blood vessels from damage.
Taming Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Inflammation and oxidative stress are pivotal contributors to aging and chronic ailments like cancer, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and arthritis. While inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or infection, chronic or excessive inflammation can harm healthy cells and tissues. Oxidative stress, on the other hand, results from an imbalance between free radicals (unstable molecules causing damage) and antioxidants (molecules neutralizing free radicals). This stress can lead to DNA damage, cell death, and tissue dysfunction.
Intermittent fasting can help mitigate inflammation and oxidative stress by modulating various cellular pathways and genes involved in these processes. Additionally, it increases the production of antioxidants like glutathione and catalase, shielding cells from free radical damage.
Elevating Brain Function and Neurogenesis
Intermittent fasting can significantly benefit brain health by enhancing both function and structure. Fasting stimulates the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein supporting the survival and growth of brain cells (neurons). BDNF also plays a crucial role in improving learning, memory, mood, and cognitive abilities. Moreover, intermittent fasting can boost neurogenesis, the creation of new neurons in the brain. This process contributes to brain plasticity (the ability to adapt) and resilience (the ability to recover from stress or injury).
Furthermore, intermittent fasting may provide protection against neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, amyloid plaques, and neuronal degeneration.
Activating Autophagy and Cellular Repair

Autophagy, a cellular process, involves breaking down and recycling damaged or unnecessary cellular components. This process is crucial for maintaining cellular health, preventing diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and infections, and plays a role in aging. As individuals age, autophagy declines, resulting in the accumulation of cellular waste and dysfunction.
Intermittent fasting can activate autophagy by depriving cells of nutrients and energy, prompting the cellular self-cleaning mechanism. This fasting-induced autophagy enhances cell quality and efficiency while eliminating harmful substances and pathogens. Additionally, intermittent fasting stimulates the repair of DNA damage, reducing the risk of mutations and cancer.
In summary, intermittent fasting is a dietary approach that focuses on when you eat rather than what you eat. This method offers numerous potential benefits, including weight loss, improved blood sugar and cholesterol levels, reduced inflammation and oxidative stress, enhanced brain function, and activation of cellular repair mechanisms. As you consider incorporating intermittent fasting into your lifestyle, consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying medical conditions. Intermittent fasting can be a powerful tool to enhance your overall health and well-being when practiced correctly.